Examples¶
Setup a store
In [1]: from tempfile import TemporaryDirectory
# You can, of course, also directly use S3, ABS or anything else
# supported by :mod:`storefact`
In [2]: dataset_dir = TemporaryDirectory()
In [3]: store_url = f"hfs://{dataset_dir.name}"
In [4]: import pandas as pd
In [5]: from kartothek.api.dataset import read_table, store_dataframes_as_dataset
In [6]: df = pd.DataFrame({"Name": ["Paul", "Lisa"], "Age": [32, 29]})
In [7]: dataset_uuid = "my_list_of_friends"
In [8]: metadata = {
...: "Name": "My list of friends",
...: "Columns": {
...: "Name": "First name of my friend",
...: "Age": "honest age of my friend in years",
...: },
...: }
...:
In [9]: store_dataframes_as_dataset(
...: store=store_url, dataset_uuid=dataset_uuid, dfs=[df], metadata=metadata
...: )
...:
Out[9]: DatasetMetadata(uuid=my_list_of_friends, tables=['table'], partition_keys=[], metadata_version=4, indices=[], explicit_partitions=True)
# Load your data
# By default the single dataframe is stored in the 'core' table
In [10]: df_from_store = read_table(store=store_url, dataset_uuid=dataset_uuid, table="table")
In [11]: df_from_store
Out[11]:
Age Name
0 32 Paul
1 29 Lisa
Eager¶
Write¶
In [12]: import pandas as pd
In [13]: from kartothek.api.dataset import store_dataframes_as_dataset
# Now, define the actual partitions. This list will, most of the time,
# be the intermediate result of a previously executed pipeline which e.g. pulls
# data from an external data source
# In our particular case, we'll use manual input and define our partitions explicitly
# We'll define two partitions which both have two tables
In [14]: input_list_of_partitions = [
....: {
....: "label": "FirstPartition",
....: "data": [("FirstCategory", pd.DataFrame()), ("SecondCategory", pd.DataFrame())],
....: },
....: {
....: "label": "SecondPartition",
....: "data": [("FirstCategory", pd.DataFrame()), ("SecondCategory", pd.DataFrame())],
....: },
....: ]
....:
# The pipeline will return a :class:`~kartothek.core.dataset.DatasetMetadata` object
# which refers to the created dataset
In [15]: dataset = store_dataframes_as_dataset(
....: dfs=input_list_of_partitions,
....: store=store_url,
....: dataset_uuid="MyFirstDataset",
....: metadata={"dataset": "metadata"}, # This is optional dataset metadata
....: metadata_version=4,
....: )
....:
In [16]: dataset
Out[16]: DatasetMetadata(uuid=MyFirstDataset, tables=['FirstCategory', 'SecondCategory'], partition_keys=[], metadata_version=4, indices=[], explicit_partitions=True)
Read¶
In [17]: import pandas as pd
In [18]: from kartothek.api.dataset import read_dataset_as_dataframes
# Create the pipeline with a minimal set of configs
In [19]: list_of_partitions = read_dataset_as_dataframes(
....: dataset_uuid="MyFirstDataset", store=store_url
....: )
....:
# In case you were using the dataset created in the Write example
In [20]: for d1, d2 in zip(
....: list_of_partitions,
....: [
....: {"FirstCategory": pd.DataFrame(), "SecondCategory": pd.DataFrame()},
....: {"FirstCategory": pd.DataFrame(), "SecondCategory": pd.DataFrame()},
....: ],
....: ):
....: for kv1, kv2 in zip(d1.items(), d2.items()):
....: k1, v1 = kv1
....: k2, v2 = kv2
....: assert k1 == k2 and all(v1 == v2)
....:
Iter¶
Write¶
In [21]: import pandas as pd
In [22]: from kartothek.api.dataset import store_dataframes_as_dataset__iter
In [23]: input_list_of_partitions = [
....: {
....: "label": "FirstPartition",
....: "data": [("FirstCategory", pd.DataFrame()), ("SecondCategory", pd.DataFrame())],
....: },
....: {
....: "label": "SecondPartition",
....: "data": [("FirstCategory", pd.DataFrame()), ("SecondCategory", pd.DataFrame())],
....: },
....: ]
....:
# The pipeline will return a :class:`~kartothek.core.dataset.DatasetMetadata` object
# which refers to the created dataset
In [24]: dataset = store_dataframes_as_dataset__iter(
....: input_list_of_partitions,
....: store=store_url,
....: dataset_uuid="MyFirstDatasetIter",
....: metadata={"dataset": "metadata"}, # This is optional dataset metadata
....: metadata_version=4,
....: )
....:
In [25]: dataset
Out[25]: DatasetMetadata(uuid=MyFirstDatasetIter, tables=['FirstCategory', 'SecondCategory'], partition_keys=[], metadata_version=4, indices=[], explicit_partitions=True)
Read¶
In [26]: import pandas as pd
In [27]: from kartothek.api.dataset import read_dataset_as_dataframes__iterator
# Create the pipeline with a minimal set of configs
In [28]: list_of_partitions = read_dataset_as_dataframes__iterator(
....: dataset_uuid="MyFirstDatasetIter", store=store_url
....: )
....:
# the iter backend returns a generator object. In our case we want to look at
# all partitions at once
In [29]: list_of_partitions = list(list_of_partitions)
# In case you were using the dataset created in the Write example
In [30]: for d1, d2 in zip(
....: list_of_partitions,
....: [
....: {"FirstCategory": pd.DataFrame(), "SecondCategory": pd.DataFrame()},
....: {"FirstCategory": pd.DataFrame(), "SecondCategory": pd.DataFrame()},
....: ],
....: ):
....: for kv1, kv2 in zip(d1.items(), d2.items()):
....: k1, v1 = kv1
....: k2, v2 = kv2
....: assert k1 == k2 and all(v1 == v2)
....:
Dask¶
Write¶
In [31]: import pandas as pd
In [32]: from kartothek.api.dataset import store_delayed_as_dataset
In [33]: input_list_of_partitions = [
....: {
....: "label": "FirstPartition",
....: "data": [("FirstCategory", pd.DataFrame()), ("SecondCategory", pd.DataFrame())],
....: },
....: {
....: "label": "SecondPartition",
....: "data": [("FirstCategory", pd.DataFrame()), ("SecondCategory", pd.DataFrame())],
....: },
....: ]
....:
# This will return a :class:`~dask.delayed`. The figure below
# show the generated task graph.
In [34]: task = store_delayed_as_dataset(
....: input_list_of_partitions,
....: store=store_url,
....: dataset_uuid="MyFirstDatasetDask",
....: metadata={"dataset": "metadata"}, # This is optional dataset metadata
....: metadata_version=4,
....: )
....:
In [35]: task.compute()
Out[35]: DatasetMetadata(uuid=MyFirstDatasetDask, tables=['FirstCategory', 'SecondCategory'], partition_keys=[], metadata_version=4, indices=[], explicit_partitions=True)
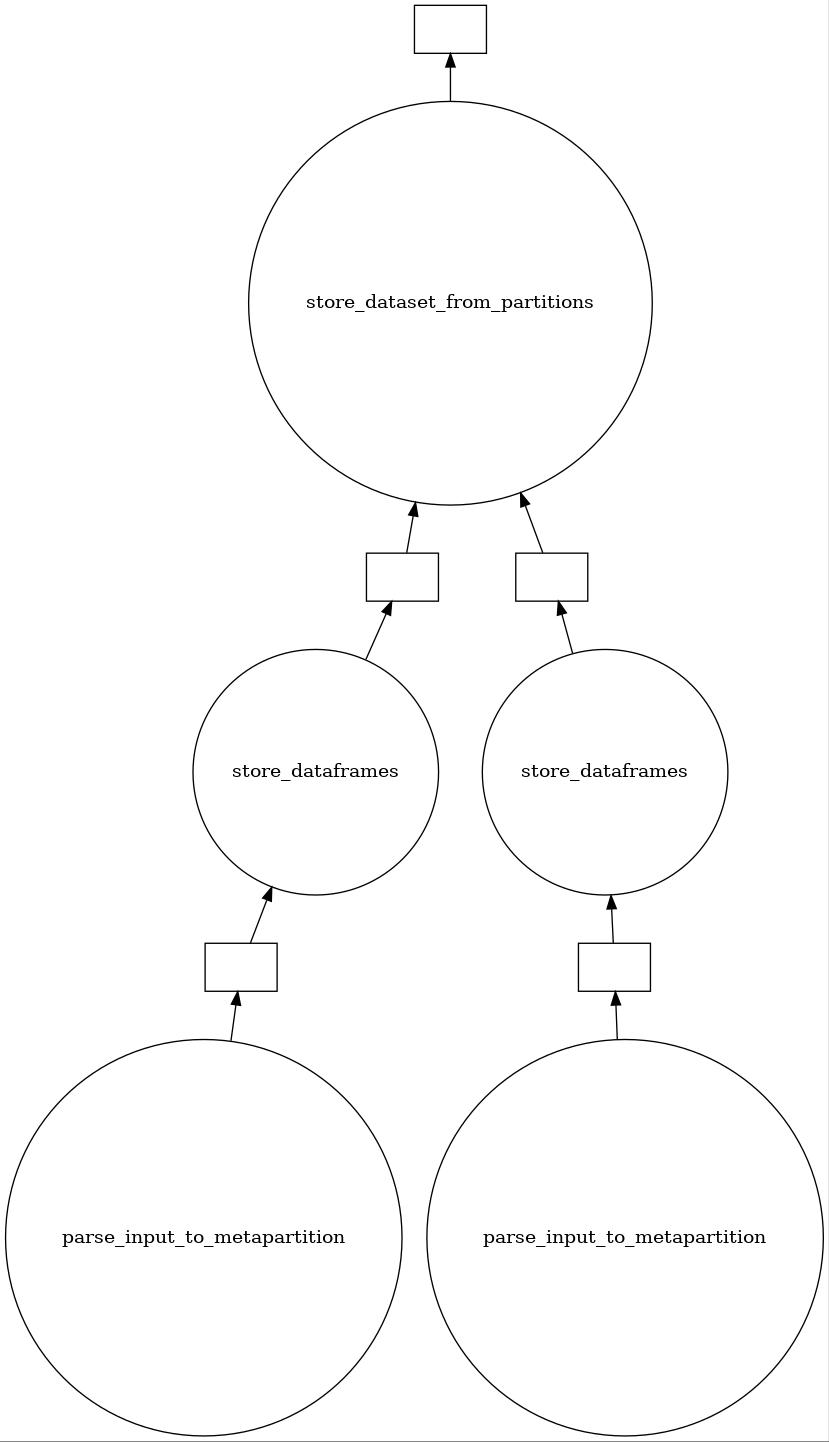
Task graph for the above dataset store pipeline.¶
Read¶
In [36]: import dask
In [37]: import pandas as pd
In [38]: from kartothek.api.dataset import read_dataset_as_delayed
In [39]: tasks = read_dataset_as_delayed(dataset_uuid="MyFirstDatasetDask", store=store_url)
In [40]: tasks
Out[40]:
[Delayed('_get_data-d93ccc29-608e-4c5a-aa1c-aff830f4b6cf'),
Delayed('_get_data-398b0e57-7f3c-41bd-a1ed-739cb00e2f02')]
In [41]: dask.compute(tasks)
Out[41]:
([{'FirstCategory': Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: [],
'SecondCategory': Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: []},
{'FirstCategory': Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: [],
'SecondCategory': Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: []}],)